Express response 主要扩展如下几个重要的方法
- res.send
- res.json
- res.jsonp
- res.sendFile
我们来看看这些分方法的实现过程,以及思考这样实现解决了哪些问题 首先,创建一个空的对象,并且使用 http.reponse 原型,保证这个对象和 http.reponse 是等效的
var res = Object.create(http.ServerResponse.prototype)
console.log(
res,
Object.getPrototypeOf(res),
Object.getPrototypeOf(Object.getPrototypeOf(res))
)打印了 res 以及其原型 和 原型的原型打印如下:
ServerResponse {}
OutgoingMessage {
_finish: [Function: _finish],
statusCode: 200,
statusMessage: undefined,
assignSocket: [Function: assignSocket],
detachSocket: [Function: detachSocket],
writeContinue: [Function: writeContinue],
writeProcessing: [Function: writeProcessing],
_implicitHeader: [Function: _implicitHeader],
writeHead: [Function: writeHead],
writeHeader: [Function: writeHead]
}
Stream {
_renderHeaders: [Function: _renderHeaders],
cork: [Function (anonymous)],
uncork: [Function (anonymous)],
setTimeout: [Function: setTimeout],
destroy: [Function: destroy],
_send: [Function: _send],
_writeRaw: [Function: _writeRaw],
_storeHeader: [Function: _storeHeader],
setHeader: [Function: setHeader],
appendHeader: [Function: appendHeader],
getHeader: [Function: getHeader],
getHeaderNames: [Function: getHeaderNames],
getRawHeaderNames: [Function: getRawHeaderNames],
getHeaders: [Function: getHeaders],
hasHeader: [Function: hasHeader],
removeHeader: [Function: removeHeader],
_implicitHeader: [Function: _implicitHeader],
headersSent: [Getter],
write: [Function: write],
addTrailers: [Function: addTrailers],
end: [Function: end],
_finish: [Function: _finish],
_flush: [Function: _flush],
_flushOutput: [Function: _flushOutput],
flushHeaders: [Function: flushHeaders],
pipe: [Function: pipe],
[Symbol(nodejs.rejection)]: [Function (anonymous)]
}这里对这些对象属性和方法有个映像,在代码中突然使用 this.statusCode 就能猜到,它是在使用原型的方法或属性
res.send 实现
res.send = function send(body) {
...
}response 扩展一个 send 方法,只接受一个返回数据字段,内部去处理 content-type、content-length、Etag、数据发送
1.1 处理 content-type
res.send = function send(body) {
var chunk = body;
var encoding;
var req = this.req;
var type;
// settings
var app = this.app;
...
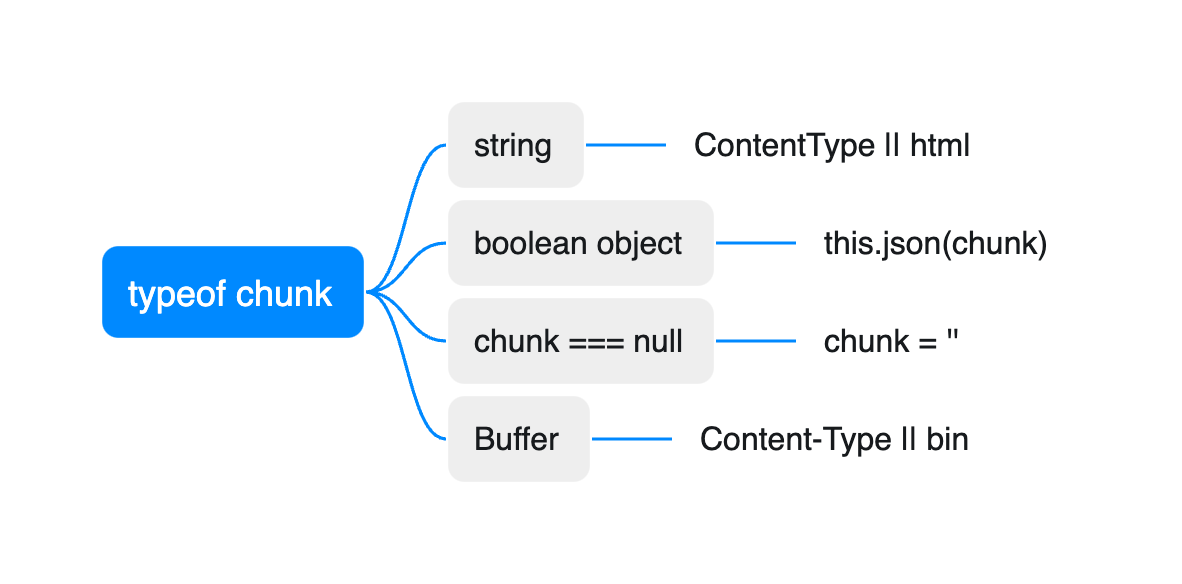
switch (typeof chunk) {
// string defaulting to html
case 'string':
if (!this.get('Content-Type')) {
this.type('html');
}
break;
case 'boolean':
case 'number':
case 'object':
if (chunk === null) {
chunk = '';
} else if (Buffer.isBuffer(chunk)) {
if (!this.get('Content-Type')) {
this.type('bin');
}
} else {
return this.json(chunk);
}
break;
}
// write strings in utf-8
if (typeof chunk === 'string') {
encoding = 'utf8';
type = this.get('Content-Type');
// reflect this in content-type
if (typeof type === 'string') {
this.set('Content-Type', setCharset(type, 'utf-8'));
}
}
}
1.2 处理 Etag
// determine if ETag should be generated
var etagFn = app.get('etag fn')
var generateETag = !this.get('ETag') && typeof etagFn === 'function'
var etag;
if (generateETag && len !== undefined) {
if ((etag = etagFn(chunk, encoding))) {
this.set('ETag', etag);
}
}etag 出的处理需要手动给 app 设置一个etag 的计算函数,etag fn 函数,用来计算etag的值,然后放在 header 中
1.3 处理 content-length
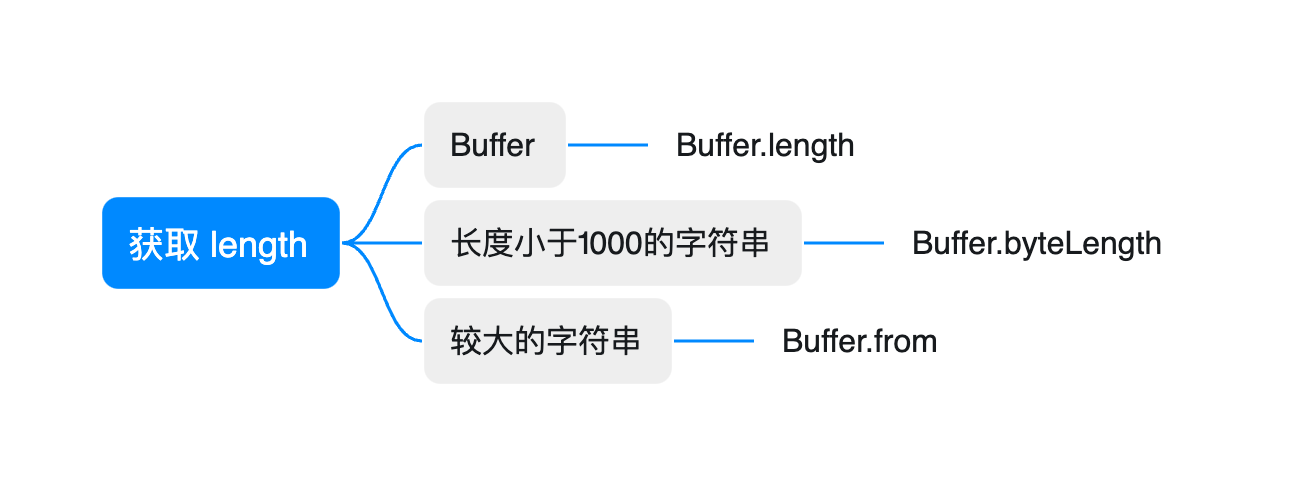
var len
if (chunk !== undefined) {
if (Buffer.isBuffer(chunk)) {
// get length of Buffer
len = chunk.length
} else if (!generateETag && chunk.length < 1000) {
// just calculate length when no ETag + small chunk
len = Buffer.byteLength(chunk, encoding)
} else {
// convert chunk to Buffer and calculate
chunk = Buffer.from(chunk, encoding)
encoding = undefined;
len = chunk.length
}
this.set('Content-Length', len);
} 这里可以补充一个知识点
这里可以补充一个知识点
在 Node.js 中,Buffer.byteLength(string[, encoding]) 和 Buffer.from(string[, encoding]).length 都可以用来获取字符串的字节长度。但是,这两者在处理大字符串时的性能有所不同。 Buffer.byteLength(string[, encoding]) 是一个同步操作,它会阻塞事件循环直到计算完成。对于大字符串,这可能会导致性能问题。 相反,Buffer.from(string[, encoding]).length 是一个异步操作,它不会阻塞事件循环。这使得它在处理大字符串时更具性能优势。 所以,如果你正在处理大字符串,使用 Buffer.from(string[, encoding]).length 可能会是一个更好的选择。
1.4 发送数据
if (req.method === 'HEAD') {
// skip body for HEAD
this.end();
} else {
// respond
this.end(chunk, encoding);
}这里不再过多解释,不理解HEAD方法的可以查一下HEAD方法
res.json 方法
res.json = function json(obj) {
var val = obj;
// settings
var app = this.app;
var escape = app.get('json escape')
var replacer = app.get('json replacer');
var spaces = app.get('json spaces');
var body = stringify(val, replacer, spaces, escape)
// content-type
if (!this.get('Content-Type')) {
this.set('Content-Type', 'application/json');
}
return this.send(body);
};理解了 send 之后,json 就很好理解,大致流程如下
 jsonp 和 sendFile 就不一一梳理了,基本原理相似,只是根据不同的数据类型,做不同的数据包装。
jsonp 和 sendFile 就不一一梳理了,基本原理相似,只是根据不同的数据类型,做不同的数据包装。
总结
从上面可以看到 response 干了下面几件事
 原来要十几行的代码 现在只需要 一个 res.send() 就能解决,大大提升了研发效率
原来要十几行的代码 现在只需要 一个 res.send() 就能解决,大大提升了研发效率

